Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation | 7 min read
Scleroderma: Causes, Symptoms, Complication, Diagnosis
Medically reviewed by
Table of Content
Synopsis
Systemic sclerosis, often known as scleroderma, is a group of uncommon disorders that cause the skin to tighten and stiffen. It can also affect the blood vessels, internal organs, and digestive tract.
Key Takeaways
- Scleroderma is an autoimmune disease that causes the body to overproduce connective tissue
- Scleroderma symptoms and indicators differ depending on which regions of the body are afflicted
- Scleroderma presently has no known treatments that can stop excessive collagen production
Scleroderma Meaning
Scleroderma, also known as systemic sclerosis, is a persistent but uncommon autoimmune condition in which dense, thick fibrous tissues replace the normal tissue. The immune system often assists in protecting the body from illness and infection. In scleroderma patients, the immune system stimulates other cells to make excessive collagen (a protein). The skin and organs get this additional collagen, which thickens and hardens (similar to the scarring process).
Scleroderma disease can affect the gastrointestinal system, lungs, heart, kidneys, blood vessels, joints, muscles, and skin. However, it often just affects the skin. Scleroderma may pose a serious risk to life in its most extreme forms.
What is the Main Cause of Systemic Sclerosis?
Scleroderma is an autoimmune disease that causes the body to overproduce connective tissue. As a result, the tissue becomes thickened or fibrotic and scars. Connective tissue is responsible for the formation of the fibers that comprise the framework that supports the body. They occur beneath the skin, surrounding the blood vessels and internal organs, and support the bones and muscles. Although genetic and environmental factors like dust allergies, toxic chemicals, etc., both may have a role. Systemic Sclerosis patients frequently originate from families where another autoimmune condition predominates.
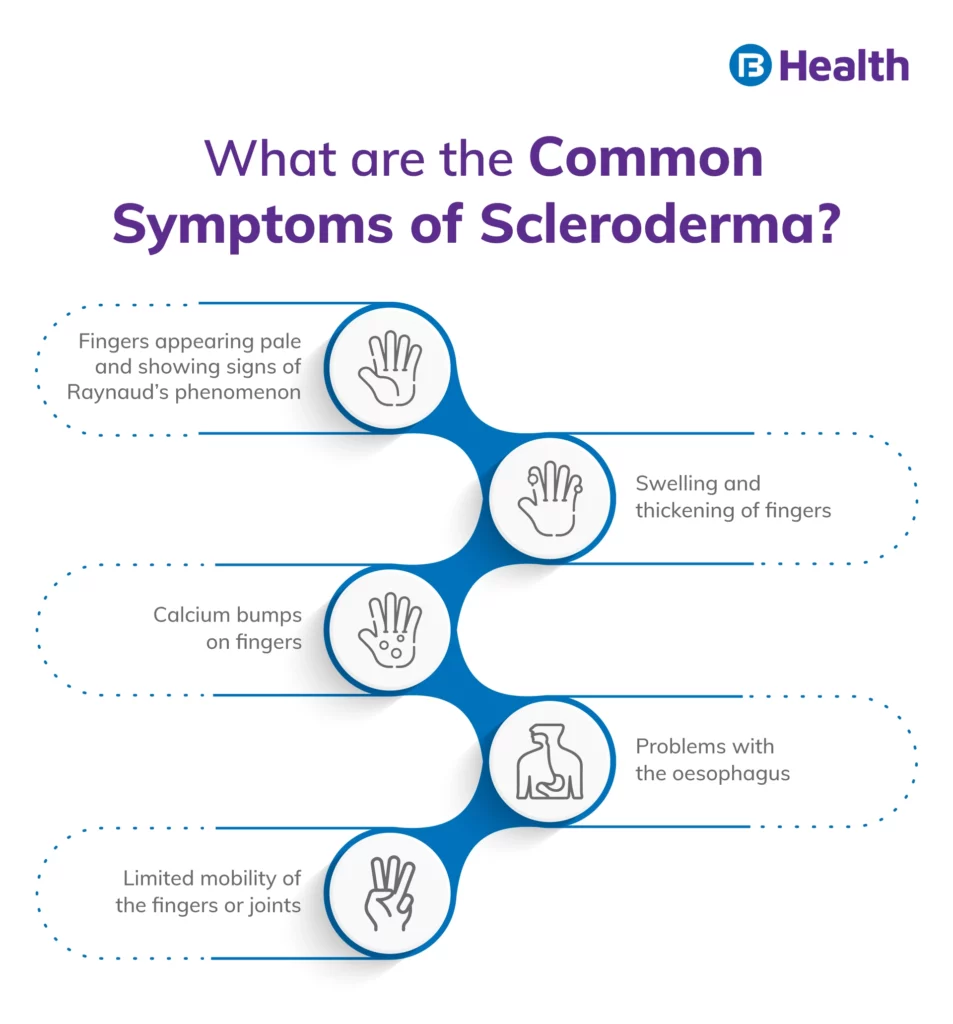
How Does Scleroderma Begin?
Scleroderma's early signs include changes in the hands and fingers, such as stiffness, tightness, and puffiness, brought on by sensitivity to cold or psychological stress. Swelling in the hands and feet is possible, especially in the morning. Following systemic sclerosis symptoms are typically present:
- Connective tissue calcium deposits
- Raynaud's disease, is a constriction of the blood vessels in the hands and feet [1]
- Issues with the esophagus, which connects the stomach and throat
- The skin on the fingers has become tight and thick
- Red spots on the face and hands
- Hands and foot swelling
- Excessive skin calcium deposition (calcinosis) [2]
- Contractual of the joints (rigidity)
- Ulcerations on the toes and fingertips
- Joint aches and stiffness
- Constant cough
- Breathlessness
- Heartburn (acid reflex)
- Swallowing difficulties
- Gastrointestinal and digestive issues
- Constipation
- Loss of weight
- Fatigue
- Loss of hair
However, symptoms will vary depending on the condition, how it affects the person, and whether it affects a single bodily component or a whole system.
Additional Read: Fungal Skin Infections
Scleroderma Treatment
Scleroderma presently has no known treatments that can stop excessive collagen synthesis. However, complications with the organ system can be treated by doctors to reduce harm and preserve functionality.
Scleroderma that is localized may go away on its own. Exfoliate skin from time to time and incorporate it into your daily routine, as it can aid in symptom management and prevent problems.
The objectives are to reduce limitations, alleviate symptoms, stop or at least delay the deterioration of the illness, and identify and treat problems as soon as possible.
Systemic sclerosis treatment is based on the patient's response to the disease:
- Blood pressure medications may facilitate blood vessel dilation. This can lessen issues with the organs, such as the lungs and kidneys
- Immunosuppressive drugs can suppress or relax the immune system
- Physical therapy may aid with pain management, mobility enhancement, and strength improvement. Splints are one type of aid that might assist with daily duties
- Laser surgery and ultraviolet light treatment may help enhance the skin's health and look
- Bisphosphonates and calcium channel blockers are used to treat calcinosis
- Macrosomia, which can occur with scleroderma and impair a person's ability to open their mouth, is treated with hyaluronidase injections.
Scleroderma treatments are still being sought after by experts, who are hopeful they will succeed. Patients must also be careful to avoid latex exposure and receive prompt latex allergy treatment if necessary.
Scleroderma Diagnosis Criteria
It is not always an easy condition to diagnose. It may initially be confused for lupus or rheumatoid arthritis due to the fact that it can affect other body parts, such as the joints [3].
After reviewing your family medical history, your doctor will perform a comprehensive physical examination. While doing this, they will be on the lookout for any of the symptoms listed above, particularly any skin darkening or thickness around the fingers and toes. Tests will be prescribed if it is thought that the patient has scleroderma to confirm the disease's severity. These tests may include the following for scleroderma diagnosis:
- Blood Tests: 95% of scleroderma patients have elevated levels of immunological factors called antinuclear antibodies [4]. Even if these antibodies are also seen in other autoimmune conditions such as lupus, testing for them in suspected scleroderma patients can help with an accurate diagnosis.
- Pulmonary Function Examinations: These examinations are used to assess how effectively the lungs are working. It is important to confirm if scleroderma has reached the lungs, where it may cause scar tissue formation, and whether it has been diagnosed or is presumed to have done so. An X-ray or computed tomography (CT scan) may be performed to examine for lung injury.
- Electrocardiogram: it can result in cardiac tissue scarring, which can induce congestive heart failure and irregular heart electrical activity. This test is carried out to determine whether the illness has impacted the heart.
- An Echocardiogram: ultrasound of the heart, is advised once every six to twelve months to check for issues, including congestive heart failure or pulmonary hypertension.
- Gastrointestinal Tests: Scleroderma can damage both the muscles of the esophagus and the intestine's walls. This can hinder the speed at which food travels through the intestines and the efficiency with which nutrients are absorbed, in addition to producing heartburn and making swallowing difficult. A procedure known as an endoscopy, which involves inserting a thin tube with a camera on its end, is occasionally used to observe the esophagus and the intestines. Manometer is a test that assesses the strength of the esophageal muscles.
- Kidney Function: Scleroderma can impact the kidneys, which can cause the protein to seep into the urine and a rise in blood pressure. In its most severe form (known as scleroderma renal crisis), a rapid rise in blood pressure may lead to kidney failure. Blood tests can be used to determine kidney function.
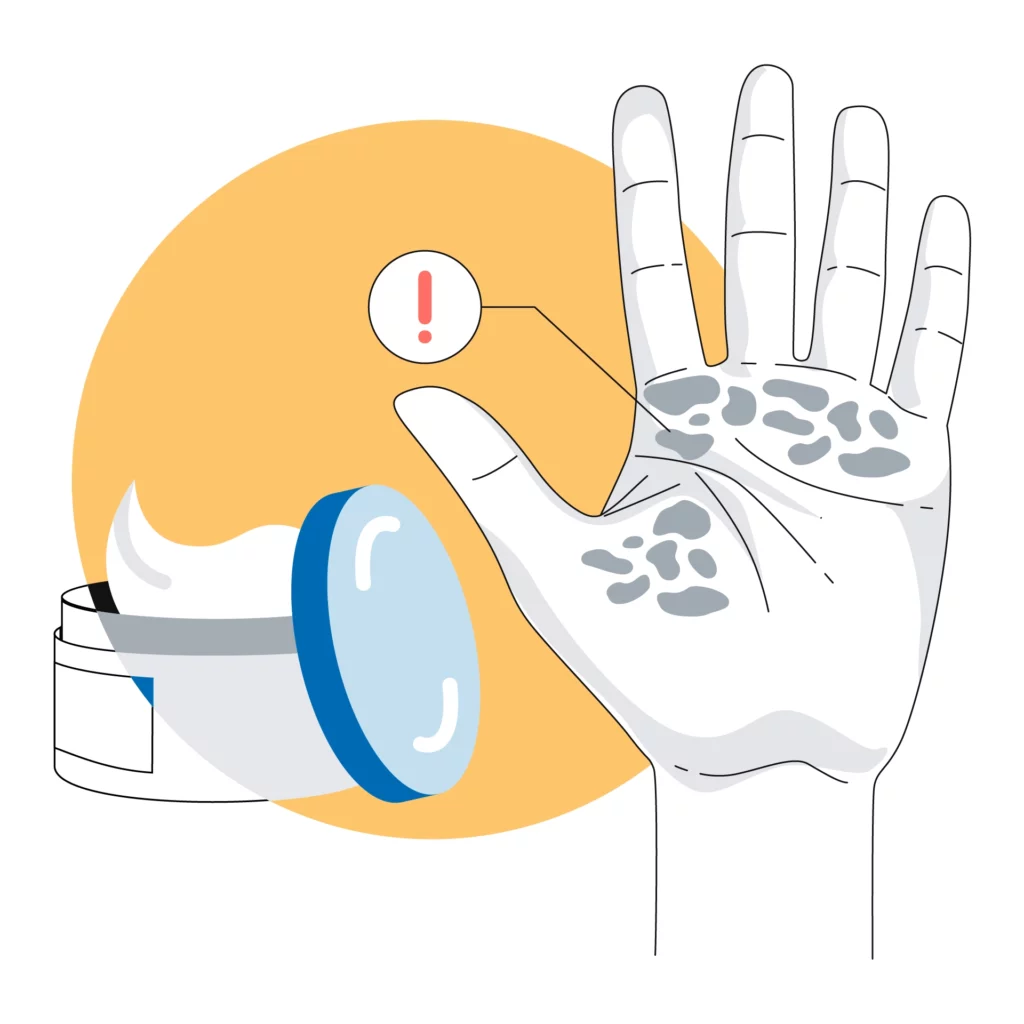
Complications Caused by Scleroderma
The severity of scleroderma complications can range from minor to life-threatening. A higher risk of cancer is also present. Other complications that might occur are:
- Movement and Flexibility Issues: As the skin tightens and swells in the hands and fingers, as well as around the mouth and face, movement may become restricted. Movement of the joints and muscles may also become more difficult.
- Raynaud's Disease: If left untreated, this condition can permanently harm the fingers and toes, leaving pits or sores in the skin and, in extreme cases, gangrene. It could be required to amputate.
- Lung Complications: Pulmonary hypertension, or high blood pressure in the artery carrying blood from the heart to the lungs, can harm the lungs permanently and impair breathing. The right ventricle of the heart could not be functioning properly. Perhaps a lung transplant is required to treat this condition.
- Kidney Damage: This can result in high blood pressure, excess protein in the urine, and hypertension. It's possible for kidney failure. Among the symptoms are headache, visual issues, seizures, shortness of breath, swelling of the legs and feet, and decreased urine output.
- Heart Arrhythmias: Heart tissue scarring can cause irregular heartbeats and congestive heart failure. Pericarditis, an inflammation of the lining around the heart, can occur in a person. This results in fluid accumulation around the heart and chest pain.
- Dental Issues: If facial skin tightening causes the mouth to become smaller, even routine dental treatment may become more challenging. The prevalence of dry mouth raises the danger of tooth decay. Changes in the gum tissue and acid reflux can erode tooth enamel and lead to teeth falling out.
- Sexual Problems: Men with scleroderma frequently have erectile dysfunction. Additionally, a woman's vaginal opening may narrow, and there may be less lubrication during sexual activity.
- Hypothyroidism: it can result in an under active thyroid, which can induce hormonal changes that slow the metabolism.
- Digestive Problems: Bloating, constipation, and other disorders may come from the esophagus's difficulty transferring food and liquids into the stomach.
The most common causes of scleroderma deaths are issues with the heart, kidneys, and lungs. It's important to remember that your physical and mental health are often directly related. Occasionally, you might require extra assistance to assist you in managing your emotions. Get in touch with Bajaj Finserv Health to get doctor consultations with psychologists or therapists who may provide you with some perspective and can aid in developing coping mechanisms, including relaxation methods.
References
- https://www.uptodate.com/contents/raynaud-phenomenon-beyond-the-basics/print#:~:text=The%20Raynaud%20phenomenon%20(RP)%20is,in%20response%20to%20cold%20temperatures.
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK448127/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12410095/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/antinuclear-antibody
Disclaimer
Please note that this article is solely meant for informational purposes and Bajaj Finserv Health Limited (“BFHL”) does not shoulder any responsibility of the views/advice/information expressed/given by the writer/reviewer/originator. This article should not be considered as a substitute for any medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always consult with your trusted physician/qualified healthcare professional to evaluate your medical condition. The above article has been reviewed by a qualified doctor and BFHL is not responsible for any damages for any information or services provided by any third party.