Cardiology | 5 min read
High Blood Pressure Vs Low Blood Pressure: A Comprehensive Guide for You
Medically reviewed by
Table of Content
Key Takeaways
- Blood pressure measuring 120/80 mmHg is usually considered normal
- Untreated hypertension can cause a stroke or heart failure
- Hypotension can result in fainting, risk of injury, and dizziness
The arteries carry the blood from the heart to other parts of the body. This blood also carries oxygen and other nutrients required for the optimal functioning of every vital organ in the body. Blood pressure is the measure of the force with which blood circulates via the arteries throughout the body. Normal blood pressure is necessary to ensure that both oxygen and nutrients are pushed through to every organ. This ensures the delivery of oxygen and white blood cells, insulin, and antibodies.
While your blood pressure changes throughout the day, severe fluctuation beyond the threshold limit of 120/80 mmHg can be harmful. While low blood pressure is not considered problematic and is temporary, high blood pressure or hypertension can cause severe and fatal health complications ranging from damaged organs to a stroke.
When it comes to understanding high blood pressure vs low blood pressure, it is important to know that high blood pressure is much more lethal and causes lasting damage. However, both high and low blood pressure are linked to mental and emotional distress. Recent studies have shown a strong link between high blood pressure and Alzheimer's, the primary cause of dementia in the elderly. Similarly, low blood pressure has shown to have a strong connection to minor psychological impairment.
Read on to know more about high BP vs low BP.
What is high blood pressure?
Blood pressure measuring 130/80 mmHg or higher is considered high blood pressure. Compared to low blood pressure, high blood pressure or hypertension has more adverse consequences. Narrowed arteries constrict the flow of blood, increasing blood pressure. This forces the heart to work harder, weakening it and eventually causing heart diseases.
The most effective way to treat high blood pressure is early detection. However, high blood pressure develops slowly over the years and does not show any symptoms. However, this does not prevent it from damaging vital organs like the kidney, brain, liver and blood vessels.
There are mainly two types of hypertension, primary hypertension and secondary hypertension. In primary hypertension, the cause of the condition is unknown. However, a combination of risk factors such as age, genetics, and environment are known to increase this condition's risk. Therefore, treatment and prevention measures include prescription medication and lifestyle changes.
Secondary hypertension has an identifiable underlying cause and treating this cause usually results in respite. Some of the common causes of secondary hypertension are kidney diseases, thyroid problems, congenital heart problems and obstructive sleep apnea.
Early diagnosis of hypertension is difficult, as it is a silent condition that develops over time. On the other hand, as the condition worsens, it manifests severe symptoms like blurry vision, nosebleeds, dizziness and headaches. These symptoms warrant immediate medical attention and treatment.
Additional Read: How to Manage and Treat High Blood PressureWhat is low blood pressure?
Low blood pressure or hypotension is not life-threatening. In some cases, low blood pressure is even desirable. A blood pressure reading lower than 90/60 mmHg is considered low blood pressure. This condition is characterized by fatigue, nausea, difficulty in concentrating and breathing, fainting, light-headedness and blurred vision. In severe cases, low blood pressure can cause shock, resulting in shallow and rapid breathing, increased pulse rate and confusion.
There are four types of low blood pressure, depending on when your blood pressure drops.
Orthostatic
This occurs when someone stands from a sitting or lying position. It can happen to anyone and lasts merely a few seconds.
Postprandial
This is a sub-type of orthostatic blood pressure that occurs after eating. It is common in an elderly person with Parkinson's disease.
Neutrally mediated
This occurs when you stand for a long time or after hearing upsetting news. This type of low blood pressure is prevalent in children.
Severe hypotension
This occurs when your body goes into shock due to an insufficient supply of oxygen and blood to the organs. This can be life-threatening if left untreated.
The risk of low blood pressure increases with age, especially in people above 65. Also, low blood pressure can be a side effect of medication for other conditions. For instance, alpha-blockers used to treat high blood pressure can increase the risk of developing low blood pressure. Furthermore, certain diseases such as diabetes, endocrine problems, severe bloodstream infections, allergic reactions like anaphylactic shock, Parkinson and heart issues can give rise to low blood pressure. Moreover, pregnancy, lack of a nutritious diet and heavy blood loss due to injury can also cause low blood pressure.
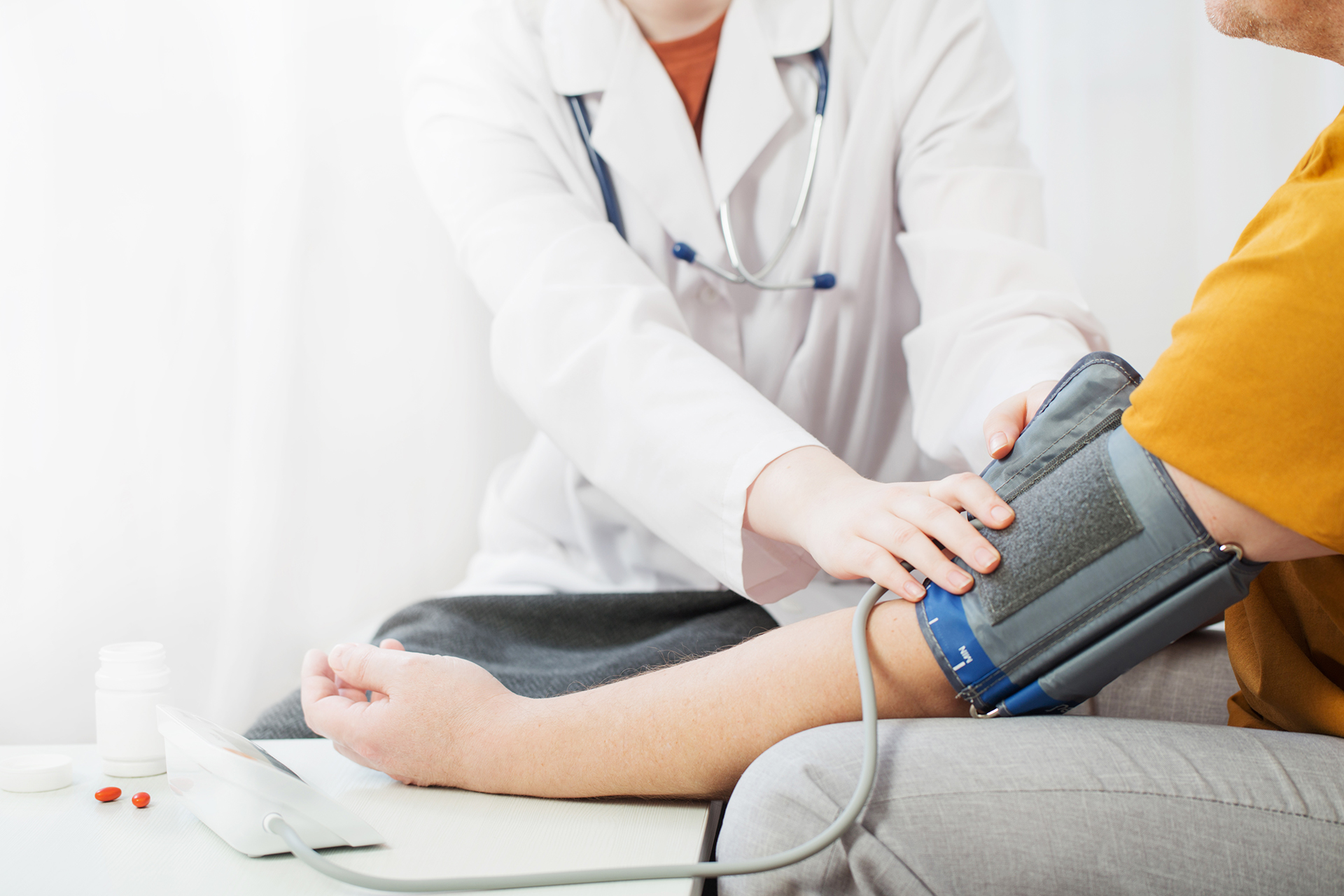
How to monitor blood pressure?
One of the best and most effective ways of preventing and treating any blood pressure, especially high blood pressure, is early detection and diagnosis. Therefore, regular monitoring of blood pressure, especially as you grow older, is necessary. Now, you can do so by either visiting your doctor or using a blood pressure monitor device at home.
How to accurately measure your blood pressure at home
Keep in mind that blood pressure measurement consists of two readings, systolic and diastolic pressure. The first reading is your systolic pressure, and the second is your diastolic pressure. Therefore, if your reading is 119/80 mmHg, then 119 is your systolic pressure, and 80 is your diastolic pressure.
Follow the steps below to get accurate blood pressure readings at home.
- Activity, stress and anxiety can increase or decrease your blood pressure. Therefore, ensure that you are relaxed and sit still while measuring your blood pressure.
- Ensure that you are sitting correctly with your back straight, feet flat on the ground, and not crossed. Then, ensure that your arm is supported on a flat surface and at heart level. Ensure that the bottom of the cuff ends above the elbow.
- Read the provided instructions carefully and measure your blood pressure at the same time every day.
As seen above, blood pressure can happen to anyone, and the best way to avoid it is to take preventive measures. These include making healthy lifestyle choices like exercising regularly, following a healthy diet and undergoing regular check-ups and screening tests. Furthermore, you should limit your consumption of meats and add more vegetables to your diet, limit or avoid alcohol consumption and smoking and cut back on sweets and sodium-heavy foods.
To get the best tips customised to you and further understand the risk of high BP vs low BP, visit the right general practitioner. Do this easily on Bajaj Finserv Health, which allows you to book appointments with specialists and the best GPs in seconds. You can also filter doctors by location, experience, timings and more, and even book video consultations. What’s more, you can keep a digital health record and explore health plans that get you discounts from top diagnostic centres, hospitals and clinics.
References
- https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.313260
- https://www.bmj.com/content/304/6819/75.abstract
Disclaimer
Please note that this article is solely meant for informational purposes and Bajaj Finserv Health Limited (“BFHL”) does not shoulder any responsibility of the views/advice/information expressed/given by the writer/reviewer/originator. This article should not be considered as a substitute for any medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always consult with your trusted physician/qualified healthcare professional to evaluate your medical condition. The above article has been reviewed by a qualified doctor and BFHL is not responsible for any damages for any information or services provided by any third party.