General Health | 6 min read
Norovirus: Symptoms, Complications, And Prevention
Medically reviewed by
Table of Content
Synopsis
Even though it is not the flu, norovirus can cause severe diarrhoea and vomiting that are occasionally referred to as stomach flu. It is very contagious and can be passed through contaminated surfaces, food, or other individuals.
Key Takeaways
- Noroviruses are a highly infectious group of related viruses
- Consuming contaminated food, untreated water and not washing your hands are some causes of contracting norovirus
- Rest, drinking plenty of water and eating a good diet can help faster recovery from norovirus
What is Norovirus?
A family of closely related viruses known as noroviruses are highly infectious. Gastroenteritis is a condition that results from infection with these viruses and affects the stomach and intestines (inflammation of the stomach and intestines).
The most frequent cause of gastroenteritis in the US is noroviruses, which are often known as "food poisoning" or "stomach bugs." Between 19 and 21 million instances of acute gastroenteritis are annually brought on by norovirus in the US, with young children and older people suffering the most.[1]
Norovirus outbreaks have been recorded in various locations, including hospitals, dining establishments, catered events, childcare facilities, and schools.
Meaning of Norovirus
When seeking the norovirus meaning, we learnt that the virus gets its name from the US city of Norwalk, Ohio, where an outbreak occurred in 1968. Infections with norovirus are more frequent in the winter. It frequently happens during outbreaks and is the root of roughly half of all food-borne illness outbreaks in the US.
Norovirus Causes
The norovirus is quite contagious. That implies that norovirus infection can spread quickly to other people. Both vomit and stools contain the virus. Therefore, you can transfer the virus from the moment you start to experience symptoms of an illness until a few days after you start feeling well. Noroviruses can survive for days or weeks on surfaces and objects.
Some of the common norovirus causes are:
- Consuming contaminated food
- Consuming untreated water
- Putting your hand to your lips after it has touched a contaminated object or surface
- Being close to someone who is sick with the norovirus
Noroviruses are challenging to eradicate since they are resistant to high and low temperatures and numerous disinfectants.
Risk factors to norovirus:
- Residing with a child who attends a preschool or daycare
- Staying at a place with lots of people, such as a hotel, cruise ship, or resort
- Living in a facility, hospital, or retirement community that is closed or mostly closed
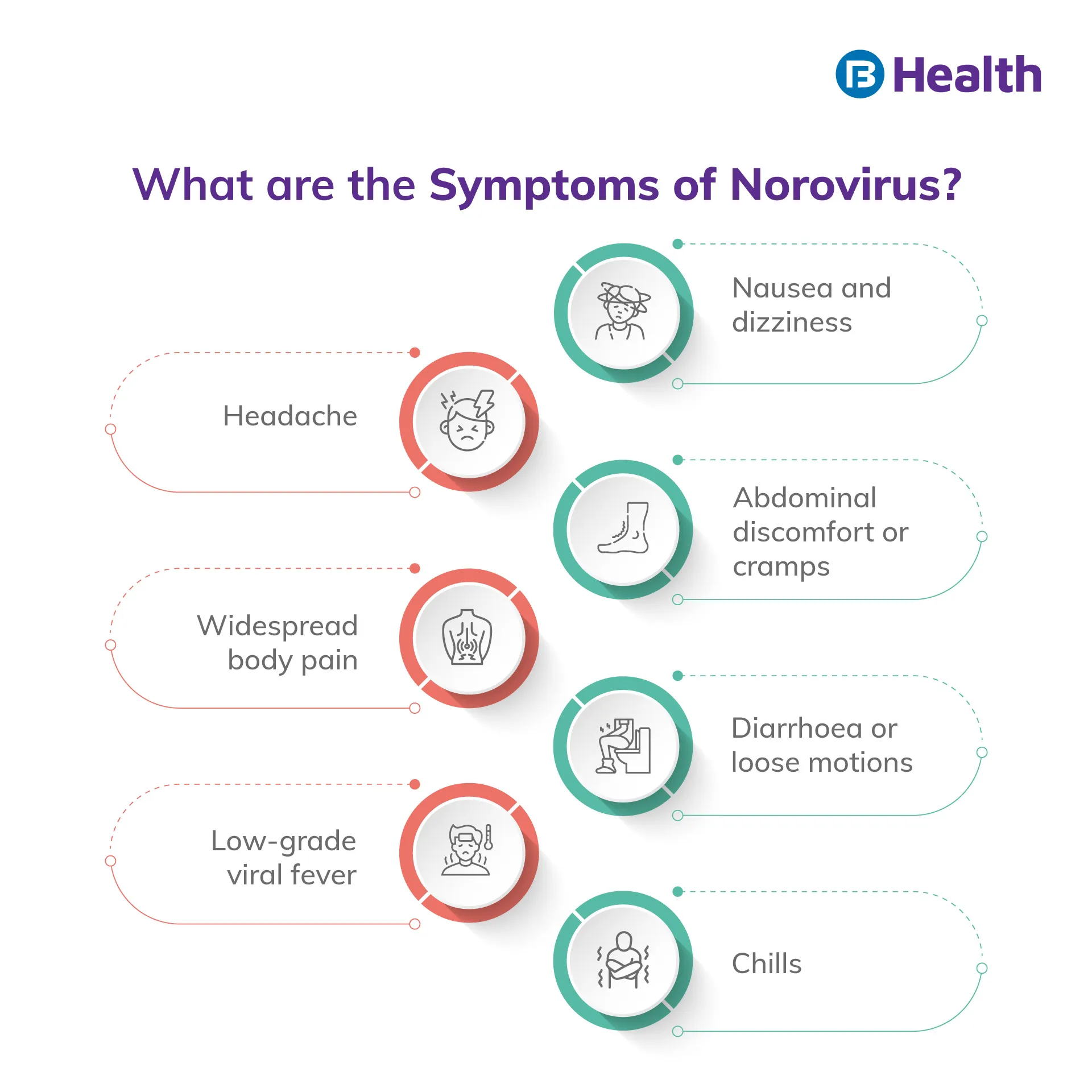
Symptoms of Norovirus
After exposure to the virus, symptoms of infection typically appear somewhere between 12 and 48 hours later. They might be minor to really severe. Norovirus symptoms include, among others:
- Nausea and dizziness
- Abdominal discomfort or cramps
- Diarrhoea or loose motions
- Chills
- Headache
- Widespread body pain
- Low-grade viral fever
The typical duration of symptoms is 24 to 72 hours. If symptoms continue after that or if you notice blood in your faeces, consult a doctor. Dehydration brought on by severe diarrhoea needs to be treated as a medical emergency. Dehydration symptoms and signs include:
- Throat and mouth are dry
- Reduced urine production or dark urine
- No urine for children in 12 hours
- Darkened eyes
- Drowsiness and exhaustion
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Uncertainty and sluggishness
- Quick heartbeat
According to estimates, the virus may occasionally—roughly 30% of the time—cause no symptoms at all. [2] Children are particularly prone to this.
Additional Read: Best Migraine Remedies in AyurvedaNorovirus Treatment
There is no specific norovirus treatment. Antibiotics won't assist because the condition is not bacterial in nature. To prevent dehydration, the primary focus of treatment is support. Here are some pointers for self-care:
- Rest: Avoid pushing yourself. Stay at home and relax
- Stay Hydrated: Drink a lot of water. Oral hydration products like Pedialyte are advised for all ages to replace electrolytes. They are essential for babies and young children
Only older kids and adults should consume sports drinks, popsicles, and broth. Avoid drinking sugary beverages because they can make diarrhoea worse. Additionally, it would be best to avoid alcoholic and caffeinated beverages.
- Maintain your diet: Infants should continue breastfeeding or formula feeding while rehydrating
As appetite increases, some healthy options for kids and adults are:
- Soups
- Simple noodles
- Rice
- Pasta
- Eggs
- Potatoes
- Bread or crackers
- New fruits
- Yoghurt
- Jell-o
- Steamed veggies
- Lean meats like fish and chicken
But make a doctor's appointment in case:
- If you can't tolerate liquids when you have a fever
- If you have severe diarrhoea which lasts longer than three days
- If your stools are bloody
- If you have a significant underlying health condition
- If you typically take prescription drugs but find it difficult to take them
- Dehydration from diarrhoea that lasts more than three days might cause serious consequences. You might need to stay in the hospital to obtain intravenous fluids
How is Norovirus Diagnosed?
Although noroviruses can be recognised from a stool sample, norovirus illness is typically diagnosed based on your symptoms. Your doctor might advise a stool test to determine whether norovirus is present if you have a compromised immune system or other medical issues.
Complications Associated With Norovirus
Norovirus infections seldom result in complications. If they do, they might involve any of the following:
- Dehydration due to a lack of fluid and an electrolyte imbalance: This is the most typical complication. It happens if you don't consume enough fluids to restore the water and salts lost in your stools (faeces) or when you've been ill (vomited). Dehydration is unlikely to happen or is likely moderate, and you will quickly recover if you can drink enough fluids. You may have a reduction in blood pressure if you are very dehydrated. Your vital organs may receive less blood as a result of this. Kidney failure may also occur if dehydration is not managed
- A case of gastroenteritis can sometimes cause irritable bowel syndrome
- Occasionally, persistent diarrhoeal symptoms can appear
How can Norovirus be Prevented?
Norovirus spreads swiftly in enclosed areas where many people congregate, including schools, cruise ships, and nursing homes. The majority of occurrences take place in the winter and early spring. You can take the following routine safety measures to lessen your risk of contracting the virus:
- Regularly wash your hands with soap and water
- Complete fruit and vegetable washing
- Comprehensive seafood preparation
But generally speaking, maintaining excellent cleanliness is necessary to lessen your risk of contracting diseases from others and stop spreading many infections to others. So the most crucial thing you and your child can do is wash their hands.
Feel free to contact Bajaj Finserv Health to speak to an expert for additional details about norovirus. In addition, you can arrange a virtual teleconsultation from the comfort of your home to get the correct knowledge on norovirus symptoms in adults and other queries so that you can enjoy a healthy life ahead.
References
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23876403/
- https://www.cdc.gov/hai/pdfs/norovirus/229110-anorocasefactsheet508.pdf
Disclaimer
Please note that this article is solely meant for informational purposes and Bajaj Finserv Health Limited (“BFHL”) does not shoulder any responsibility of the views/advice/information expressed/given by the writer/reviewer/originator. This article should not be considered as a substitute for any medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always consult with your trusted physician/qualified healthcare professional to evaluate your medical condition. The above article has been reviewed by a qualified doctor and BFHL is not responsible for any damages for any information or services provided by any third party.





