General Physician | 5 min read
Will Herd Immunity Against COVID-19 Really Work? A Guide
Medically reviewed by
Table of Content
Key Takeaways
- Herd immunity is also known as community immunity
- Measles vaccination is one herd immunity example in recent times
- Make sure you are vaccinated and follow all safety measures
With COVID-19 cases peaking once again, researchers are leaving no stone unturned to find an effective way to curb its spread. One possible way to do as per some experts is to achieve herd immunity. Also known as community immunity, herd immunity is the indirect protection offered when a large part of the population is immune to a specific disease.
To achieve herd immunity against COVID, 75-80% of the whole population must develop immunity against the virus. But this looks far from possible due to many challenges. Immunity can be gained through vaccinations or past exposure to the virus. Immunity by allowing the population to be exposed to the spread of the virus is not a favorable way forward as it can lead to fatal consequences [1].
To know why achieving herd immunity may or may not be possible, read on.
Additional Read: Herd Immunity and COVID-19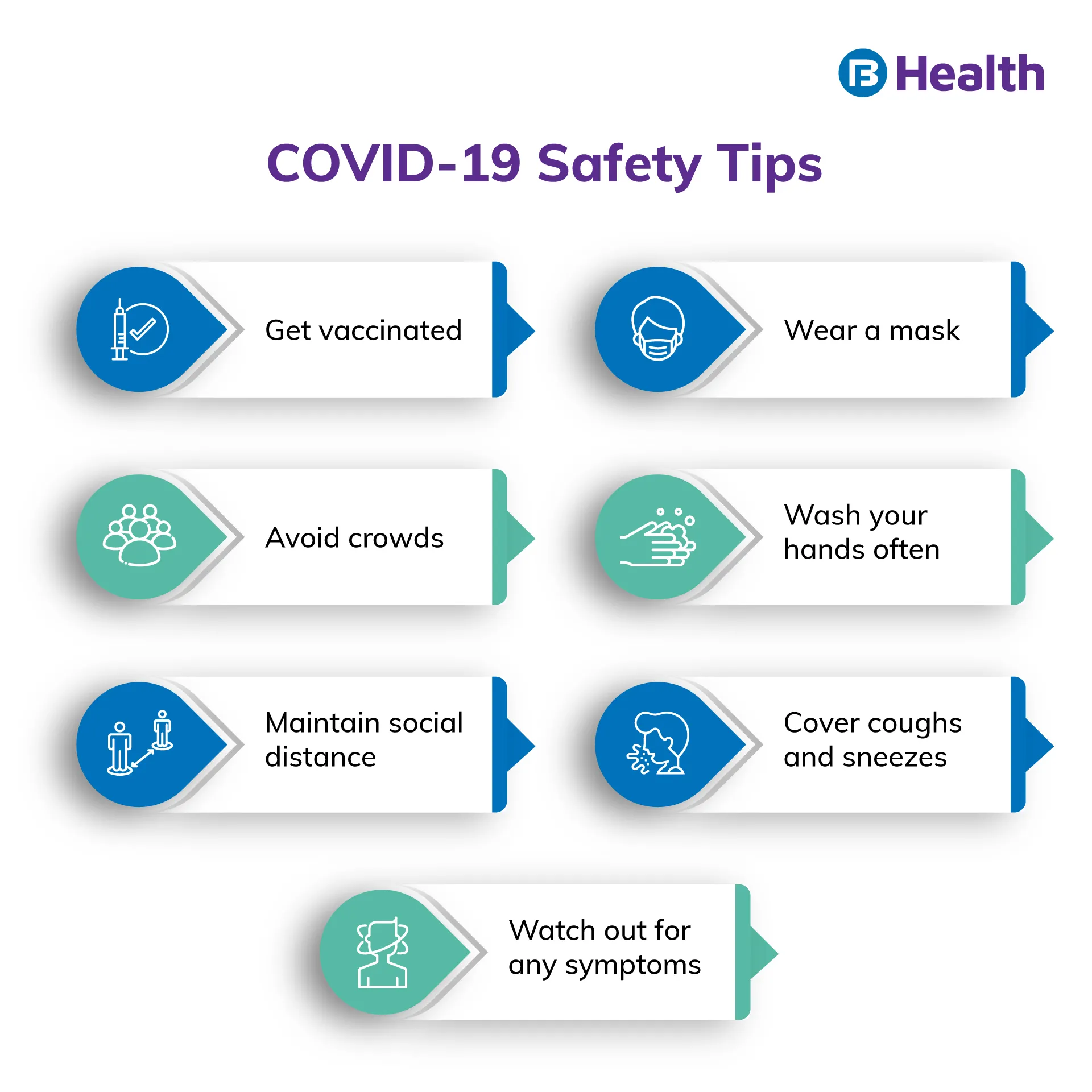
Reasons Why Herd Immunity Against Covid-19 Is Challenging
Uncertainty of Protection
Herd immunity can be effectively achieved with a transmission-blocking vaccine. The COVID-19 vaccines such as Pfizer and Moderna are effective at preventing symptomatic disease. But it is still not clear whether these vaccines can prevent the spread of the virus or if they can protect you from getting infected.
This uncertainty is a hurdle for achieving herd immunity. In the absence of vaccines that block the transmission, the only sensible thing to do is to vaccinate everyone. Experts believe that even a 70% vaccine transmission-blocking effectiveness can make a difference [2].
Hesitation in Taking Vaccines
Several people around the world are skeptical or do not believe in vaccination. There could be several reasons for such thoughts and behavior. These include fears of possible risks and belief in myths about vaccination. If the percentage of vaccinated people is below the threshold of reaching herd immunity, preventing the spread of the virus is difficult. People not getting vaccinated can pose a risk of rapid transmission of the COVID-19 virus.
Uneven Distribution
Experts believe that a well-coordinated roll-out of vaccines all over the world could have stopped the spread of COVID-19. However, this is very unlikely in reality on a global scale. There is a huge gap in the distribution of vaccines among and within countries.
For instance, if one community receives vaccinations at a high rate and the surrounding areas do not, a possible risk of outbreak still remains when the population mixes. So, it is vital that vaccines get rolled-out and administered evenly to protect a large population. This can help bring the pandemic under control.

New Variants
New variants of the SARS-CoV-2 are being reported from various corners of the world. For instance, omicron is the latest mutated version of the virus that has been reported [3]. With new variants on the rise, their transmission rate and response to the existing vaccines are not clear.
These variants can be more transmissible and dangerous than the previous ones. The distribution and allocation hurdles of the vaccines often leave enough time for new variants to emerge and spread. Thus, it is important to reduce such hurdles and curb the spread of the virus at the earliest.
Immunity Period
Herd immunity against COVID can be achieved through natural infection and vaccines. Those infected with the SARS-CoV-2 develop some immunity to the virus. However, there is no conclusive data on how long this immunity lasts. Experts believe that immunity gained through infection decreases over time. If this immunity lasts for a few months, it may pose a challenge in delivering the vaccines. Besides, understanding how long vaccine-based immunity lasts and if boosters are required is necessary.
Human Behavior
Human behavior has a role to play in achieving the herd immunity threshold or acting as a hurdle. For instance, as more people get vaccinated, the number of interactions will increase. This changes the herd immunity equation. Vaccination has its own drawbacks. Your risk remains the same as you interact with more people even with a high vaccine efficacy rate. Thus, ignoring COVID-19 precautionary measures and practicing unhealthy habits can impact this negatively.
How Can Herd Immunity Against COVID-19 Become Effective?
The spread of COVID-19 can be stopped or slowed down when a large percentage of the population becomes immune. In fact, it requires at least 70% of the population to have achieved immunity to bring the infection rate down [4].
However, this level depends on various factors including how infectious the virus is and human behavior. The spread of many infections can be prevented by breaking the chain of transmission. It helps protect unvaccinated people, older adults, children, babies, people with weak immunity, and those with existing health diseases.
Herd immunity can come into effect for some diseases when 40% of the population becomes immune. However, in most cases, around 80 to 95% of people need to be immune to stop the spread. A good herd immunity example is the measles vaccination. It requires 19 out of 20 people to get vaccinated to stop the disease. If everyone tries to understand the importance of immunization and take precautionary measures, achieving herd immunity and controlling the spread is possible.
Additional Read: Different Immunity TypesDo not take COVID-19 lightly and make sure you practice all means to stay safe. Pay no heed to all the myths surrounding COVID-19 vaccination and get yourself jabbed. You can book a vaccination slot using the vaccine finder on Bajaj Finserv Health. You can also book an online doctor consultation on the platform. This way, you can get all your health queries regarding vaccination and herd immunity answered.
References
- https://www.who.int/news-room/questions-and-answers/item/herd-immunity-lockdowns-and-covid-19
- https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-021-00728-2
- https://www.who.int/news/item/28-11-2021-update-on-omicron
- https://www.jhsph.edu/COVID-19/articles/achieving-herd-immunity-with-COVID19.html
Disclaimer
Please note that this article is solely meant for informational purposes and Bajaj Finserv Health Limited (“BFHL”) does not shoulder any responsibility of the views/advice/information expressed/given by the writer/reviewer/originator. This article should not be considered as a substitute for any medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always consult with your trusted physician/qualified healthcare professional to evaluate your medical condition. The above article has been reviewed by a qualified doctor and BFHL is not responsible for any damages for any information or services provided by any third party.





