Women's Health | min read
Vaginal Yeast Infection: Causes, Early Symptoms and Treatment
Medically reviewed by
Table of Content
Synopsis
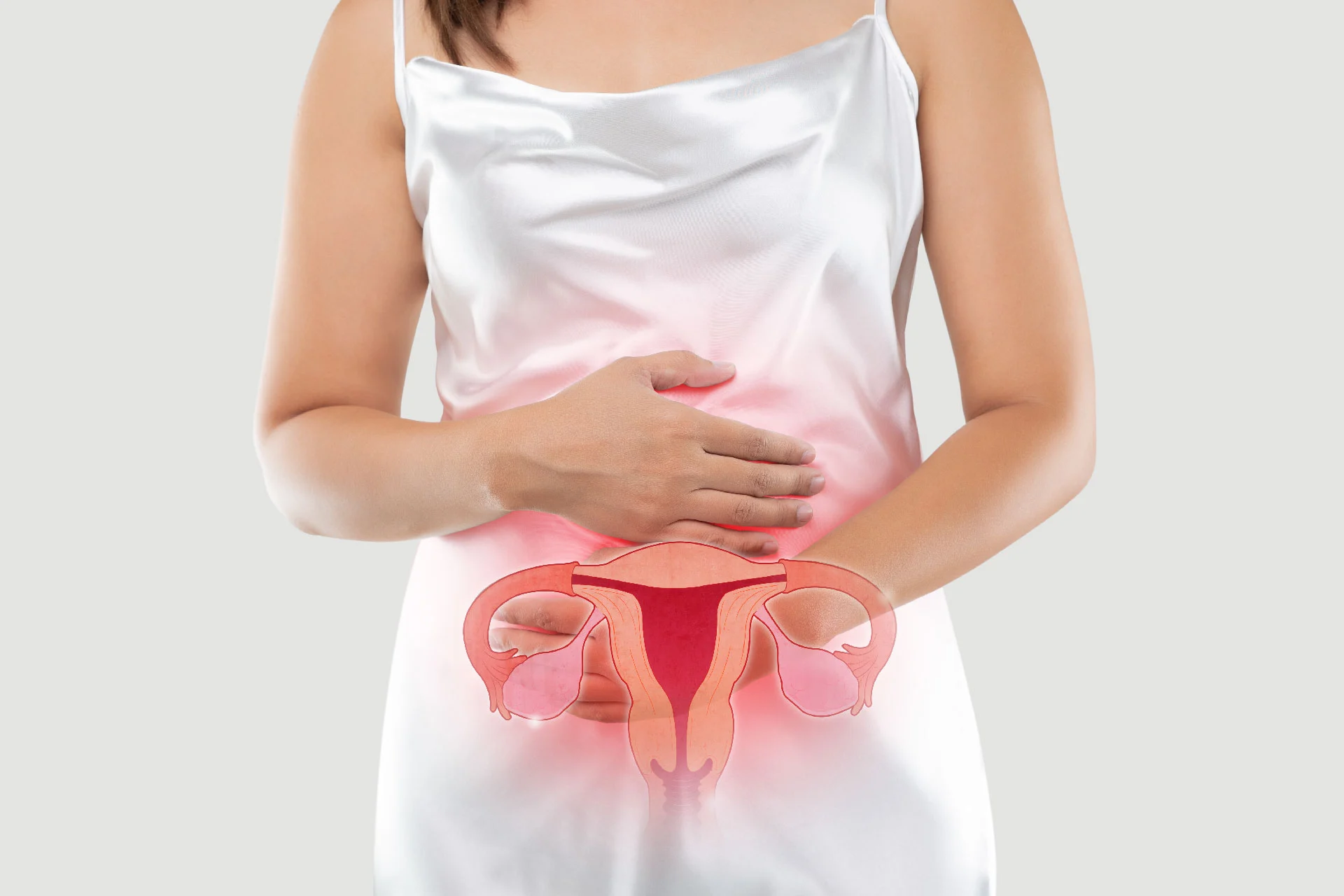
A vaginal yeast infection is a condition among people with a vagina. The condition is also referred to as candidiasis, as it is caused by a yeast named candida. If the natural balance of candida and vaginal bacteria gets affected, it can lead to the overgrowth of the candida yeast, causing vaginal yeast infection.
Key Takeaways
- Vaginal yeast infection is more common before menopause and after puberty
- Such infections can be caused by antibiotics and hormonal changes
- Treatment of vaginal yeast infection consists of oral or topical medications
What is a Vaginal Yeast Infection?
A vaginal yeast infection is a condition among people with a vagina. The condition is also referred to as candidiasis, as it is caused by a yeast named candida. Note that some bacteria and candida yeast cells are normal in a healthy vagina. However, if the bacteria inside your vagina grow out of balance, it can lead to the multiplication of yeast, eventually resulting in vaginal yeast infection. The condition usually comes with severe discomfort, swelling, and itching.
Note that vaginal yeast infection is not considered a sexually transmitted infection. Though the disease may be transmitted through sexual contact, sexually inactive women may also get infected with vaginal yeast. Usually, a few days of treatment can help relieve vaginal infection symptoms [1]. However, in chronic cases, an extended treatment may be required.
Who is Prone to Vaginal Yeast Infection?
Anyone with a vagina is at risk of getting a vaginal yeast infection, especially if they have just reached puberty or entered the premenopausal phase. Certain physiological conditions can also make you prone to vaginal yeast infection, but undergoing vaginal infection treatment is simple.
Additional Read: Fungal Skin Infection
What Causes Vaginal Yeast Infection?
Several factors can lead to abnormal growth of bacteria in your vagina, such as:
- Antibiotic Medications: Though antibiotics are supposed to treat infections in your body, they may also destroy the healthy bacteria in your vagina, which can cause an overgrowth of yeast
- A feeble immune system: If you have existing conditions such as AIDS, medications can reduce the activity of your immune system. Apart from this, cancer treatments such as radiation therapy and chemotherapy can also weaken your immune system
- High blood sugar: Having glucose in your urine can impact the bacteria in your vagina
- Pregnancy and hormonal changes: Factors that affect the hormone levels in your body can increase candida production in your vagina. These include pregnancy, taking contraceptive pills, and the usual changes in your menstrual cycle
Vaginal Yeast Infection Symptoms
With vaginal yeast infection, you may experience the following symptoms:
- A burning sensation around the vagina and vulva during urination and sex
- Continuous swelling around the vagina and vulva
- Painful intercourse
- White vaginal discharge as thick as cottage cheese
- Fragile skin, which leads to small cuts around your vulva
The symptoms of vaginal yeast infection may resemble those of other related conditions, such as vaginal dryness. If you encounter any similar symptoms, it is wise to consult a gynaecologist as soon as possible.
Additional Read: What is Vaginal Douching?Diagnose Vaginal Yeast Infection
Doctors diagnose vaginal yeast infections by listening to your symptoms and examining your vulva and vagina. They may also take a sample of your vaginal discharge for a tab test to check for any abnormalities. These will help determine the type of vaginal yeast infection and its treatment method.
Vaginal Yeast Infection Treatments
Usually, doctors recommend antifungal medications for the treatment of vaginal yeast infections. What medications will work for you depends on the severity of your infection. Doctors study your symptoms and discharge samples and recommend the best medications based on them.
The role of antifungal medications is to stop the overgrowth of yeast in your body. Your doctor may recommend either oral or topical medications. While oral medications can be swallowed with water, topical medications need to be applied around your vulva or placed inside your vagina. Apart from medications, doctors may also give you certain guidelines to follow during the treatment procedure. For example, they may ask you to abstain from sexual intercourse when the treatment is on. It is because penetrative sex can further irritate your infected skin.
Preventions
It is wise to adhere to the following measures to keep vaginal yeast infection at bay:
- Avoid douching, as it can affect the natural balance of bacteria and yeast in the vagina
- Don’t use feminine deodorants, scented sanitary pads or tampons
- Wear cotton underwear and easy-fitting clothes
- Change your wet clothing, such as a bathing suit, as soon as possible
- Work towards keeping your blood sugar level normal
- Use water-based lubricants while having sex
Early Symptoms of Vaginal Yeast Infection
Take a look at a few early symptoms you may experience in case of a vaginal yeast infection:
- A burning or itching sensation around your vagina
- Difficulty in passing bowel
- A painful sensation when you urinate
- Spotting or bleeding
- Thighs or lower back burning with pain
- Vaginal dryness
- A constant pressure on your vagina
- Swollen lymph nodes in your groin
- Red and swollen skin around the vagina
- A thick, odourless discharge that appears like cottage cheese
- Painful sensation in the vagina during and after sexual activity
Though the treatment of vaginal yeast infection is simple, it is wise not to delay consultation as that can lead to other women's health issues. In case of the slightest discomfort in or around your vagina, you can book a quick online doctor consultation on Bajaj Finserv Health. Prioritize vaginal hygiene for your sexual and overall well-being, and keep infections at bay!
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK543220/
Disclaimer
Please note that this article is solely meant for informational purposes and Bajaj Finserv Health Limited (“BFHL”) does not shoulder any responsibility of the views/advice/information expressed/given by the writer/reviewer/originator. This article should not be considered as a substitute for any medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always consult with your trusted physician/qualified healthcare professional to evaluate your medical condition. The above article has been reviewed by a qualified doctor and BFHL is not responsible for any damages for any information or services provided by any third party.