Diabetes | 5 min read
Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes: How Are They Different?
Medically reviewed by
Table of Content
Key Takeaways
- The difference between type 1 and type 2 diabetes
- Understand type 2 diabetes and pregnancy
- Know what to eat or avoid & get our diabetes diet plan
As of 2019, one in six Indians suffer from diabetes. While China has the most diabetics in the world, India is also a global diabetes hotspot, coming in at second place. Though alarming, the numbers aren’t likely to go down any time soon. This is because diabetes is largely a lifestyle disease, brought on by a high-pressure, fast-paced life, characterized by minimal or nil physical activity, poor diet and obesity.
In India, type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes are most prevalent, and when you delay their diagnosis or management, they can cause complications. So, it is best to familiarize yourself with the difference between type1 and type 2 diabetes, their symptoms, and how to address them.
Type 1 and type 2 diabetes: Broad differences
To understand the difference between type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus, you must know how the two impact your body differently.
Type 1 diabetes is defined by a complete absence or lack of insulin in the body. This is because of an auto-immune response where your body’s immune system attacks the cells in your pancreas that are responsible for production of insulin. Unfortunately, not much is known about why this happens. Experts are of the opinion that environmental factors and exposure to certain viruses could cause your body’s immune system to act this way, in addition to genetics. Type 1 diabetes develops mostly in children, and in India it is believed to affect 97,000+ children. That said, in rare cases it may impact adults too.
Additional Read: Know more about Type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetesOn the other hand, the main difference between type1 and type 2 diabetes is that when you have type 2 diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, your body produces insulin insufficiently, or is not able to use insulin in an optimal manner. In case of the latter, your pancreas are likely to produce even more insulin. Courtesy of unutilized insulin, glucose accumulates in the bloodstream. Lifestyle factors are largely to blame for type 2 diabetes, and it mainly affects those who are middle-aged or older.
Difference between type 1 and type 2 diabetes symptoms
Type 1 and type 2 diabetes symptoms aren’t vastly different from one another. The key signs to watch out for include excessive thirst, frequent urination, increased hunger, and weight loss. Type 1 diabetes weight loss is especially sudden. Apart from these key symptoms, patients may experience fatigue, nausea, blurry vision, dizziness, irritability and slow healing of cuts and wounds.
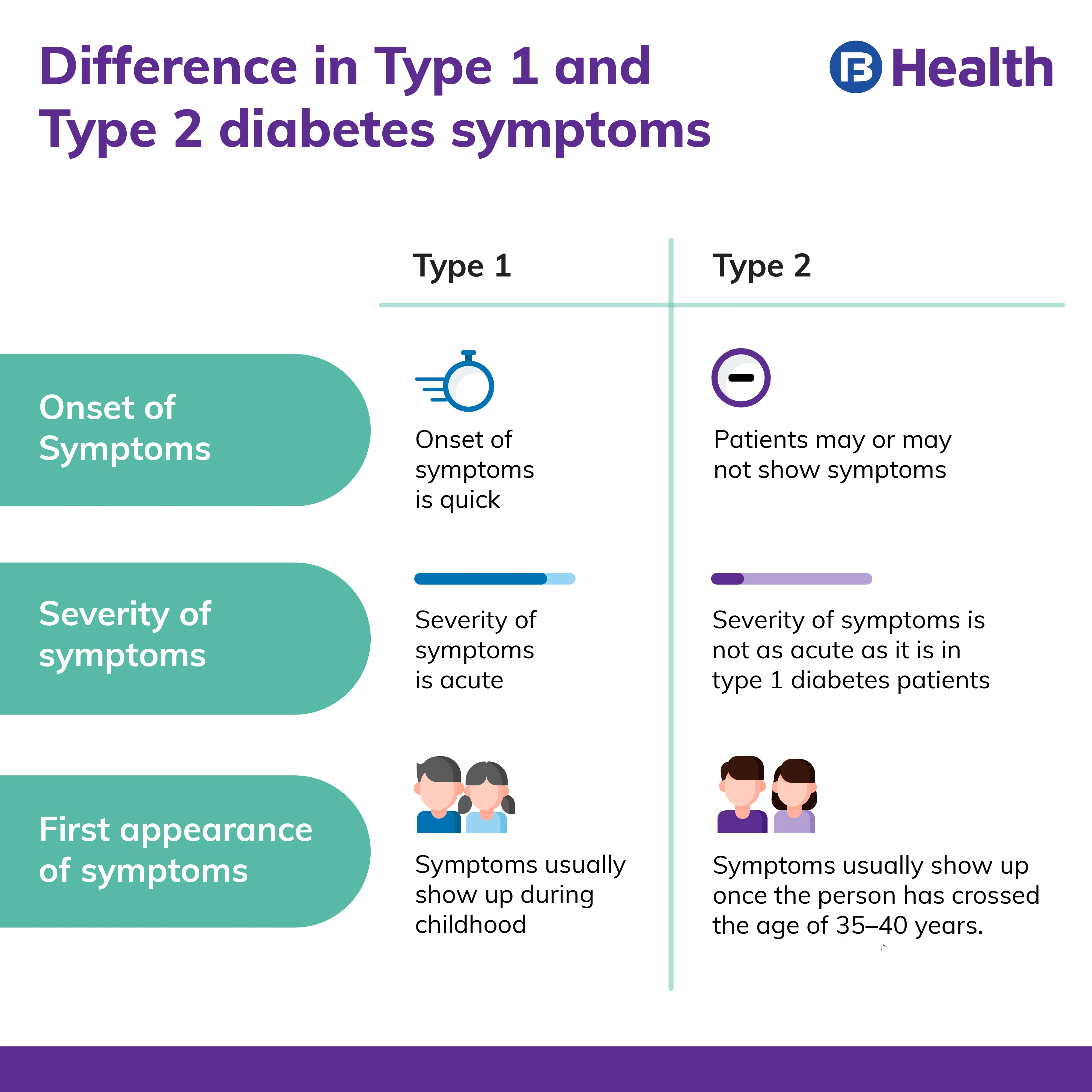
The difference lies in how these symptoms manifest themselves in type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes patients. Take a look at how this varies below.
| Difference in manifestation of type 1 and type 2 diabetes symptoms | ||
| Type 1 | Type 2 | |
| Onset of symptoms | Onset of symptoms is quick | Patients may or may not show symptoms |
| Severity of symptoms | Acute | Less acute than type 1 |
| First appearance of symptoms | Symptoms usually show up during childhood | Symptoms usually show up once the person has crossed the age of 35–40 years. However, research has found that the incidence of type 2 diabetes is increasing in children. |
Type 1 and type 2 diabetes differ as far as treatment goes as well. Type 1 diabetes patients have to inject insulin or use a type 1 diabetes insulin pump. Type 2 diabetes is treated via medication, especially medicines that fall under the GLP 1 analog class, along with exercise and diet control.
Pregnancy and Type 2 diabetes
In a nutshell, having type 2 diabetes can cause complications in your pregnancy. Therefore, when planning a baby, it’s best to discuss type 2 diabetes and pregnancy complications with your doctor. He/she will ensure that the medicines that you are taking are safe to be consumed during pregnancy, but more importantly, will tell you if you can safely proceed with conception. Optionally, he/she will advise you to bring your diabetes under control before you conceive.
Additionally, you doctor will tell you whether you need to see a gynaecologist who specialises in treating women who have type 2 diabetes and are looking to have a baby. It’s also a good idea to consult with a nutritionist and fitness expert to control your diabetes pre- and post-conception, without being overly dependent on medication. If you protect yourself from diabetes you can avail diabetes health insurance.
Diabetes diet plan
Diabetics can manage their blood sugar levels to a great extent by controlling what they eat. For type 1 diabetics, apart from eating right, timing meals with insulin doses is important. As a thumb rule, both type 1 and type 2 diabetes benefits from the consumption of low GI (Glycaemic Index) foods. In a type 1 diabetes diet plan, this is especially beneficial as the slow and steady release of sugar gives the injected insulin ample time to take effect.
Type 1 and type 2 diabetics should focus on eating:
- Complex carbohydrates such as whole wheat, quinoa, oatmeal, buckwheat and brown rice
- Plant-based proteins such as beans, legumes and tofu
- Plenty of non-starchy vegetables such as leafy greens, eggplant, zucchini, cauliflower, broccoli, beans and mushrooms
- Eggs, dairy and lean meats
- Healthy fats from nuts like almonds, walnuts and hazelnuts; seeds such as pumpkin, chia and sunflower seeds; vegetables like avocados and seafood such as salmon and tuna
Your type 2 or type 1 diabetes diet plan should exclude refined sugar, processed carbohydrates such as white bread or pasta, processed foods, foods containing unhealthy fats (such as trans fats or animal fat) and bottled beverages.
It is important to check in with a specialist to manage diabetes periodically, and this is easy to do with the Bajaj Finserv Health App. Using it, you can find the right doctor in a timely manner and understand important issues, be it type 2 diabetes mellitus pathophysiology or must-haves in a type 1 diabetes diet plan. The app not only allows you to find the right specialist, but also book in-person or video consults instantly. You can even get deals and discounts from partner diagnostic centres, hospitals and clinics and use other app features to address your health holistically. Download the app for free from the Play Store or App Store to explore all these benefits yourself.
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4413385/
- https://www.canadianjournalofdiabetes.com/article/S1499-2671(13)00044-0/fulltext
Disclaimer
Please note that this article is solely meant for informational purposes and Bajaj Finserv Health Limited (“BFHL”) does not shoulder any responsibility of the views/advice/information expressed/given by the writer/reviewer/originator. This article should not be considered as a substitute for any medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always consult with your trusted physician/qualified healthcare professional to evaluate your medical condition. The above article has been reviewed by a qualified doctor and BFHL is not responsible for any damages for any information or services provided by any third party.